Cybersecurity researchers have exposed a wide variety of techniques adopted by an advanced malware downloader called GuLoader to evade security software.
“New shellcode anti-analysis technique attempts to thwart researchers and hostile environments by scanning entire process memory for any virtual machine (VM)-related strings,” CrowdStrike researchers Sarang Sonawane and Donato Onofri said in a technical write-up published last week.
GuLoader, also called CloudEyE, is a Visual Basic Script (VBS) downloader that’s used to distribute remote access trojans such as Remcos on infected machines. It was first detected in the wild in 2019.
In November 2021, a JavaScript malware strain dubbed RATDispenser emerged as a conduit for dropping GuLoader by means of a Base64-encoded VBScript dropper.
Recent GuLoader samples unearthed by CrowdStrike have been found to exhibit a three-stage process wherein the VBScript is designed to deliver a next-stage that performs anti-analysis checks before injecting shellcode embedded within the VBScript into memory.
The shellcode, besides incorporating the same anti-analysis methods, downloads a final payload of the attacker’s choice from a remote server and executes it on the compromised host.
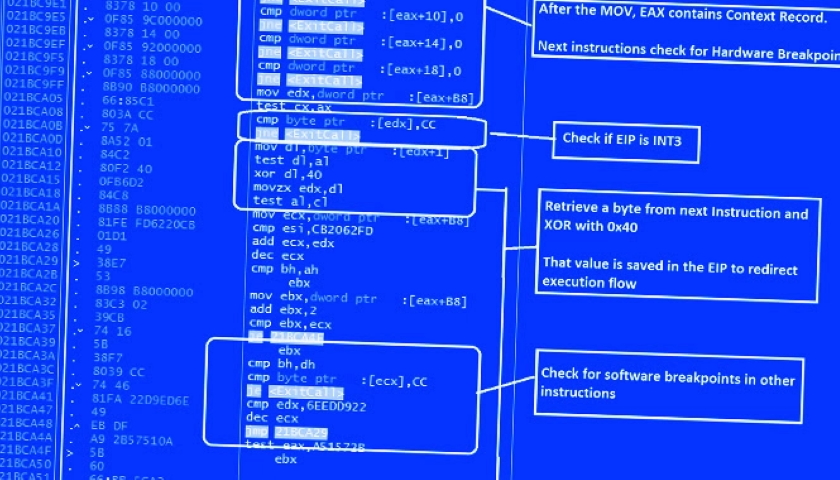
“The shellcode employs several anti-analysis and anti-debugging tricks at every step of execution, throwing an error message if the shellcode detects any known analysis of debugging mechanisms,” the researchers pointed out.
This includes anti-debugging and anti-disassembling checks to detect the presence of remote debuggers and breakpoints, and if found, terminate the shellcode. The shellcode also features scans for virtualization software.
Read more: thehackernews.com