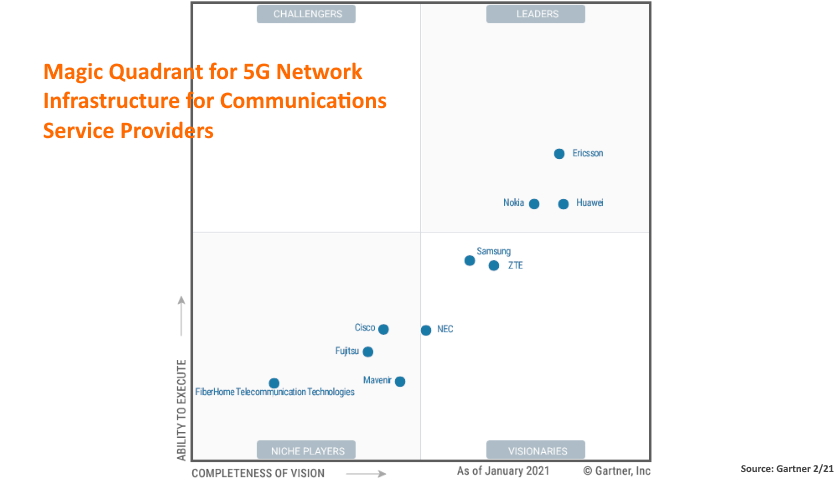
Nokia and Huawei joined Ericsson on Gartner’s list of 5G leaders.
In its latest 5G “magic quadrant” assessment, Gartner labeled Ericsson as the standout network infrastructure and communications service provider, placing it ahead of China’s Huawei and Finland’s Nokia, the only other companies that the Gartner report labeled as “leaders” in the field.
Some of Ericsson’s particular strengths, as detailed by Gartner, include its improvements having to do with dynamic spectrum sharing (DSS) and Uplink Booster, as well as the vendor’s August 2020 claim to 100 commercial 5G agreements with unique CSPs.
“Based on our counting,” stated the report, “Ericsson also possesses the largest number of 5G deals, which can be derived from its strong product portfolio and execution capabilities.”
Lastly, Gartner also pointed to Ericsson’s RAN equipment, in place since 2015 and most recently selected by United Arab Emirates’ du, that can be upgraded to 5G New Radio (NR) capability via software update, delivering a unique level of flexibility that resulted in a faster 5G rollout for its customers.
Despite flexibility when it comes to RAN equipment upgrades, Ericsson has faced particular criticism from CSPs about its lack of flexibility on other areas. For instance, CSPs have had to align with Ericsson’s features, roadmap and delivery priorities, rather than the other way around.
Further, when compared to some of its competitors, Ericsson, according to Gartner, suffers from a narrower radio unit portfolio and slower feature support.
“For example,” the report continued, “this includes the number of massive MIMO products, IBW 400 MHz massive MIMO and 5G microcell.”
The report also provided a broader picture of the global 5G rollout, referencing the GSA’s estimate that as of August 2020, more than 90 3GPP-compliant 5G networks in 38 countries/territories had been commercially launched. according to GSA.
While Ericsson, Huawei and Nokia were the only vendors to achieve “leader” status, Samsung, ZTE, and NEC were deemed “visionaries,” and Cisco, Fujitsu, Mavenir, and FiberHome Telecommunication Technologies were considered to be “niche players.”
Source: rcrwireless.com